Differences Between Cheetah Vs Leopards : Differences Between Cheetah Vs Leopards How frequently do you mistake a cheetah for a leopard or a leopard for a cheetah? It’s likely that you make this mistake the majority of the time, and you’re not alone. Many people all over the world are unable to distinguish between cheetahs and leopards, and they frequently get them mixed up. When they see a cheetah, they mistake it for a leopard, and the reverse is also true. This is because these two animals are extremely confusing; they physically look the same but differ when you look carefully and clearly.
Both cheetahs and leopards are considered to be members of the “big cat” family. If you’re lucky, you might get to see one of them during your next African wildlife safari tour, but be careful not to confuse them because they resemble one another more than you might think. Even though they have a similar appearance, cheetahs and leopards have a number of distinct physical and behavioral traits. Despite this, many individuals are unable to differentiate between them.

Because they are difficult to distinguish, we will provide you with a guide and some straightforward explanations in this article that distinguishes the two. And after reading it, you will be an expert at telling the difference between a cheetah and a leopard, as well as learn some interesting facts about both that may be useful at your next African wildlife safari tour.
How can you tell a cheetah from a leopard? What are the primary distinctions between leopards and cheetahs? Those are probably the types of questions that cross your mind frequently. The following are the top 10 key distinctions between cheetahs and leopards that you should be aware of in order to be able to tell them apart when you come across or notice them on your Tanzania safari in Africa.
- THE COAT (cheetah vs leopards)
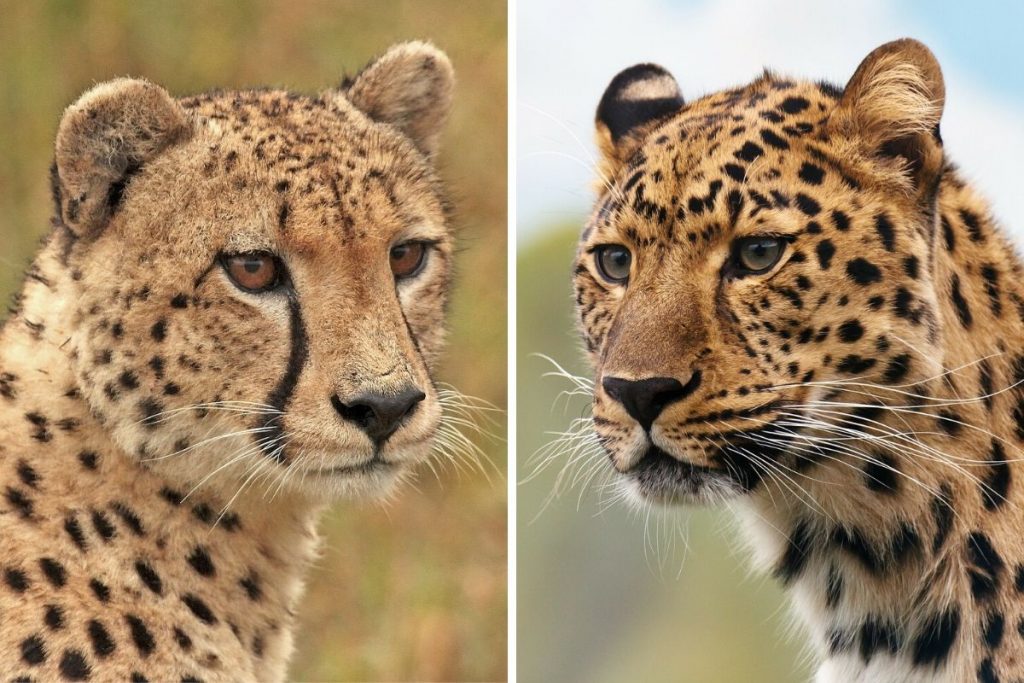
Since both cheetahs and leopards have skin coverings, people frequently confuse these two species. However, one of the characteristics that may be utilized to tell them apart, if done correctly, is their coats. To start, the fur coats of a cheetah and a leopard have some significant differences. Everything is in its place simply put, leopards have rosettes while cheetahs have spots. A cheetah’s body is covered with distinct, solid, round or oval black markings. However, the leopard has a more intricate pattern made up of rosettes, which are unevenly shaped spots gathered together to give it a rose-like pattern. By replicating the movement of grass and shadows, the leopard’s pattern aids in camouflaging while it hunts. The color of a cheetah’s and a leopard’s fur coats is another minor distinction. In contrast to a leopard, whose fur is more yellow in hue, cheetahs have tan-colored fur.
- THE FACE AND HEAD (cheetah vs leopards)
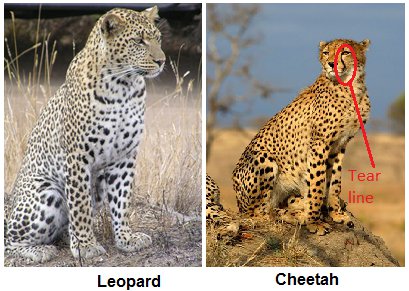
The face and head can also be used to distinguish between cheetahs and leopards. The primary distinction between the two that can be clearly observed by glancing at their faces is that a leopard lacks the black “tear marks” line that a cheetah has that extends from the inner corners of their eyes down the sides of their nose to their mouth.
When cheetahs are out hunting during the day, this black stripe on their faces helps deflect the sun’s glare. In essence, a cheetah’s own take on sunglasses. A cheetah’s head is shaped differently from a leopard’s. A leopard has a longer, extended head with dark, blackish patches on the muzzle, compared to a cheetah’s short, well-rounded head. Additionally, compared to leopards, which have a stronger jaw and teeth that can break through bones and let them pull their prey up trees, cheetahs have smaller teeth and jaws with a wider nasal cavity to facilitate quick breathing while traveling at maximum speeds.
- THE BODY SHAPE AND SIZE (Leopard vs cheetah)
Another external characteristic that can be utilized to distinguish between a cheetah and a leopard is their size and body form. Although they are the smallest of the cats, leopards are stronger and bulkier than cheetahs. Compared to a leopard, which is stronger and bulkier, a cheetah is taller and has a more slender frame. The fastest land mammal, a cheetah, is built for speed and can attain speeds of up to 112-120 km/h (70mph).
Due to their long bodies, thin stomachs, high chests, long legs for effective acceleration, and flexible spines to allow for swift changes in direction when pursuing prey, cheetahs are able to reach maximum speeds. Leopards can climb trees with ease thanks to their short, powerful legs. Leopards can pull their prey up trees because of their larger neck and shoulder muscles. Cheetahs typically weigh 54 kg for males and 43 kg for females. Leopards weigh between 30 and 40 kg for females and 60 to 70 kg for males.
- CLAWED AND BAREFOOT (cheetah vs leopard).
Cheetahs can accelerate and move at an incredible rate thanks to their large back feet. Leopards can climb up trees and hoist their prey away from scavengers because of their larger front feet. The claws of a cheetah and a leopard are another important distinction. Cheetahs can turn quickly and accelerate quickly thanks to their non-retractable claws. Leopards must have retractable claws for climbing trees and leaping on prey.
- TAIL (Cheetah vs Leopards).
The tail is another small distinction between a cheetah and a leopard. Another distinctive physical feature is the flatter curve of cheetah tails. Cheetahs can steer and maintain balance when running at high speeds thanks to the flattened tail, which serves as a rudder. In order to maintain balance while climbing up and down trees, leopards have rounder tails.
- HUNTING TECHNIQUES (cheetah vs leopards)
Given that cheetahs and leopards hunt for food in quite different ways, this is still another key distinction that can aid in making the distinction between the two. Leopards are nocturnal cats; they often hunt more frequently and are more active at night. In addition to having wide pupils to maximize light absorption, they have a huge number of light-sensitive cells in their eyes that help them detect movement and shape in the dark.
Cheetahs hunt largely during the day because they are diurnal animals. Despite this, you can occasionally see leopards hunting during the day if the opportunity arises, and cheetahs hunting by the light of a full moon.
Leopards are predators who stalk prey before pinning them. They spend a lot of time lying low on the ground, stalking their prey until they are close enough to spring on it and kill it by leverage.
High-speed cheetahs swipe at their prey’s hind legs to trip them rather than leaping on them to bring them to the ground.
Cheetahs typically drag their victims across land to a place that is isolated or has some cover once they have made a kill. They consume food quickly because they lack the power to fend off stronger predators like lions and hyenas who might try to steal their prey. Instead, leopards utilize their powerful bodies to pull their prey up a tree and along the ground so they may consume it at their leisure, safe from other predators.
- HUNTING TIME (Cheetah vs Leopards)
Cheetahs and leopards may forage for food at different times and places. While leopards often hunt at night, cheetahs prefer to hunt during the day (however, leopards will also occasionally hunt during the day if an opportunity presents itself). Leopards have an edge since they have a lot of light-sensitive cells in their eyes that can see less color and easily identify movement and shape in the dark. The leopard’s eyes have a wide pupil that lets in a lot of light, allowing it to see well at night as it goes on a hunt for prey. Again, in contrast to leopards, which employ their camouflage and prefer to hunt in more thickly forested areas where it is easier to hide, cheetahs prefer to hunt in wide expanses, giving them more room to attain top speeds.
- SPEED (cheetah vs leopards)
The cheetah moves far more quickly than the leopard. The world’s fastest terrestrial mammal is the cheetah. A cheetah can sprint from 0 to 103 km/h in 3 seconds and can accelerate quickly to 120 km/h (70 mph). However, while not being recognized for their speed, leopards can accelerate and travel short distances at rates of up to 60 km/h (37 mph).
- HABITAT AND CONDUCT (cheetah vs leopards)
While leopards are nocturnal and move more at night, cheetahs are diurnal and so move more during the day. To facilitate hunting, cheetahs prefer to live in wide grasslands, savannas, and dense foliage. Both leopards and cheetahs typically live alone. But occasionally, male cheetahs would band together into coalitions of two to three. Except when caring for their offspring, female cheetahs live alone. Mother cheetahs typically remain close to their kids. Female leopards are solitary creatures as well, but before going their own ways, they will take care of the young and teach them how to hunt.
- LIFE CYCLE (Cheetah vs leopards)
As opposed to leopards, which can live up to 12–17 years, cheetahs typically live up to 8–10 years in the wild. Unlike leopards, which mate year-round, cheetahs typically only mate during the dry season. Compared to female cheetahs, female leopards’ gestation periods range from 90 to 105 days. Compared to leopard cubs, cheetah cubs have a poorer survival rate. Cheetah cubs are more vulnerable to wildlife predictions because their mothers may leave them alone for a long time while they go food hunting. In contrast to leopards, who give birth to litters of just two to three pups at a time, cheetahs typically have litters of four to six cubs.
Conclusion, as you can see, although a cheetah and a leopard may appear similar at your eyes, they are actually very different animals with distinctive physical and behavioral characteristics. You can differentiate them using the features mentioned above, but the simplest way is to look for the “black tear strip/line” that runs down the cheetah’s face. This line extends from the cheetah’s inner eye down toward its mouth. Leopards, on the other hand, do not have these black tear strips on their faces.
WHERE CAN YOU SEE CHEETAHS AND LEOPARDS AND WHEN IS THE BEST TIME TO SEE THEM?
Both cheetahs and leopards are African wild animals that can be found and spotted in various African protected areas and national parks, such as the Serengeti National Park in Tanzania, the Ngorongoro Conservation Area in Tanzania, the Masai Mara National Reserve in Kenya, the Kruger National Park in South Africa, the Sabi Sands Game Reserve in South Africa, and the Queen Elizabeth National Park in Uganda.
When is the best time to visit Africa to see cheetahs and leopards? Cheetahs and leopards can be seen at any time of year, but during the Great wildebeest migration season of east Africa in the Serengeti and Masai Mara national reserves, you have a good chance of seeing them in action hunting wildebeest and other migrating species like zebras and gazelles.

